How To Connect Video Camera To Computer For Live Streaming
Video Streaming in Web Browsers with OpenCV & Flask
Streaming alive videos from IP Cameras or Webcam with Computer Vision
You lot took the problem of installing a webcam or a surveillance camera at your home, or office or any place that you own. Plainly, yous would want to be able to watch the alive stream of the video anyplace and anytime you like.
Well-nigh of the people utilize IP cameras (Internet Protocol cameras) instead of CCTV (Airtight-Circuit Television) for surveillance purposes as they take a much college resolution and reduced toll for cabling. You tin can discover the detailed differences between both these systems here. In this article we volition be focusing on IP cameras.
IP photographic camera, is a type of digital video camera that receives control information and sends image data via an IP network and require no local recording device. Most IP cameras are RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) based and is therefore "not supported" natively in internet browsers.
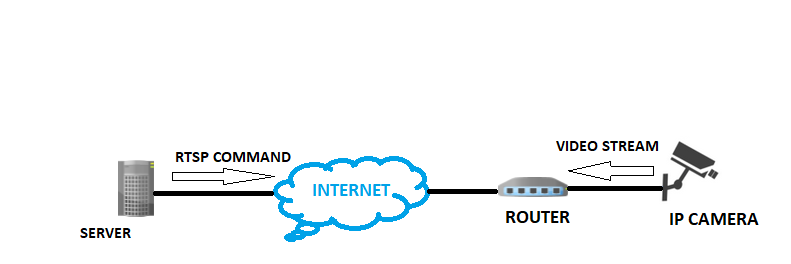
So how do y'all utilise your web browser to view the live streaming ?
In this article we will learn how to do that using Computer Vision.
Computer Vision is an interdisciplinary field that deals with how computers can be made to gain a high-level understanding from digital images or videos.
For implementing the computer vision part we volition utilise the OpenCV module in Python and to display the live stream in the web browser nosotros will utilise the Flask web framework. Before diving into the coding part let usa offset know well-nigh these modules briefly. If yous are already familiar with these modules, yous can directly jump to the next section.
According to the Wikipedia, Flask is a micro web framework written in Python. It is classified as a microframework because it does non require detail tools or libraries. It has no database brainchild layer, class validation, or any other components where pre-existing tertiary-party libraries provide mutual functions.
According to GeeksForGeeks, OpenCV is the huge open-source library for the computer vision, automobile learning, and prototype processing and at present it plays a major part in real-time performance which is very important in today's systems.
Step1- Install Flask & OpenCV :
Yous tin can use the 'pip install flask' and 'pip install opencv-python' command. I use the PyCharm IDE to develop flask applications. To easily install libraries in PyCharm follow these steps.
Step2- Import necessary libraries, initialize the flask app :
We will now import the necessary libraries and initialize our flask app.
#Import necessary libraries
from flask import Flask, render_template, Response
import cv2
#Initialize the Flask app
app = Flask(__name__) Step3- Capture Video using OpenCV :
Create a VideoCapture() object to trigger the camera and read the first paradigm/frame of the video. We can either provide the path of the video file or utilize numbers to specify the utilise of local webcam. To trigger the webcam we pass '0' as the argument. To capture the live feed from an IP Camera we provide the RTSP link as the argument. To know the RTSP address for your IP Camera go through this — Finding RTSP addresses.
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0) '''
for ip camera use - rtsp://username:countersign@ip_address:554/user=username_password='password'_channel=channel_number_stream=0.sdp' for local webcam use cv2.VideoCapture(0)
'''
Step4- Calculation window and generating frames from the camera:
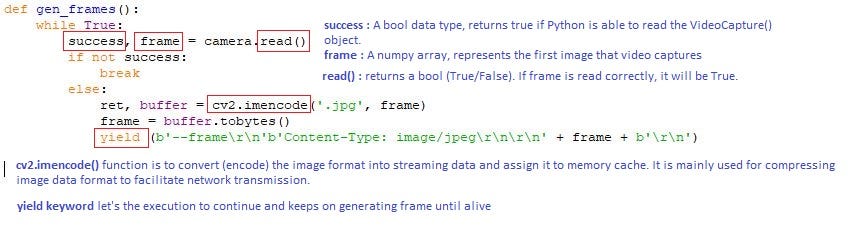
The gen_frames() function enters a loop where information technology continuously returns frames from the camera as response chunks. The function asks the photographic camera to provide a frame then it yields with this frame formatted as a response chunk with a content type of prototype/jpeg, every bit shown above. The code is shown below :
Step5- Ascertain app route for default page of the web-app :
Routes refer to URL patterns of an app (such as myapp.com/home or myapp.com/well-nigh). @app.route("/") is a Python decorator that Flask provides to assign URLs in our app to functions easily.
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html') The decorator is telling our @app that whenever a user visits our app domain (localhost:5000 for local servers) at the given .route(), execute the alphabetize() function. Flask uses the Jinja template library to return templates. In our awarding, we will use templates to render HTML which will display in the browser.
Step6- Ascertain app road for the Video feed:
@app.road('/video_feed')
def video_feed():
render Response(gen_frames(), mimetype='multipart/10-mixed-supervene upon; boundary=frame') The '/video_feed' route returns the streaming response. Because this stream returns the images that are to exist displayed in the web folio, the URL to this route is in the "src" aspect of the image tag (see 'alphabetize.html' beneath). The browser will automatically keep the prototype chemical element updated by displaying the stream of JPEG images in it, since multipart responses are supported in most/all browsers
Let's have a wait at our index.html file :
<body>
<div course="container">
<div class="row">
<div course="col-lg-8 offset-lg-2">
<h3 grade="mt-5">Live Streaming</h3>
<img src="{{ url_for('video_feed') }}" width="100%">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body> Step7- Starting the Flask Server :
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=Truthful) app.run() is called and the web-awarding is hosted locally on [localhost:5000].
"debug=True" makes sure that we don't require to run our app every fourth dimension we makes changes, nosotros can merely refresh our web page to see the changes while the server is withal running.
Projection Structure :
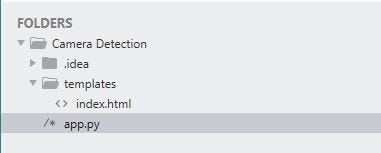
The project is saved in a folder called "Camera Detection". Nosotros run the 'app.py' file. On running this file, our application is hosted in the local server at port 5000.
Yous can simply type "localhost:5000" on your web browser to open up your spider web-application after running 'app.py'
- app.py — This is the Flask application we created to a higher place
- templates — This binder contains our 'index.html' file. This is mandatory in Flask while rendering templates. All HTML files are placed nether this folder.
Permit's see what happens when we run 'app.py' :
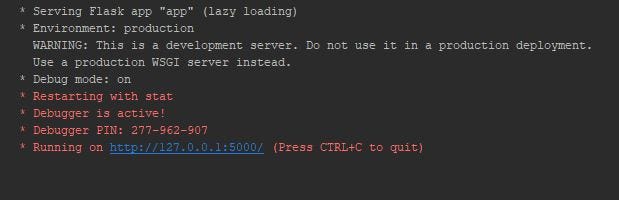
On clicking on the provided URL, our web browser opens upwards with the live feed. Since I used VideoCapture(0) above, the webcam feed is displayed on the browser:
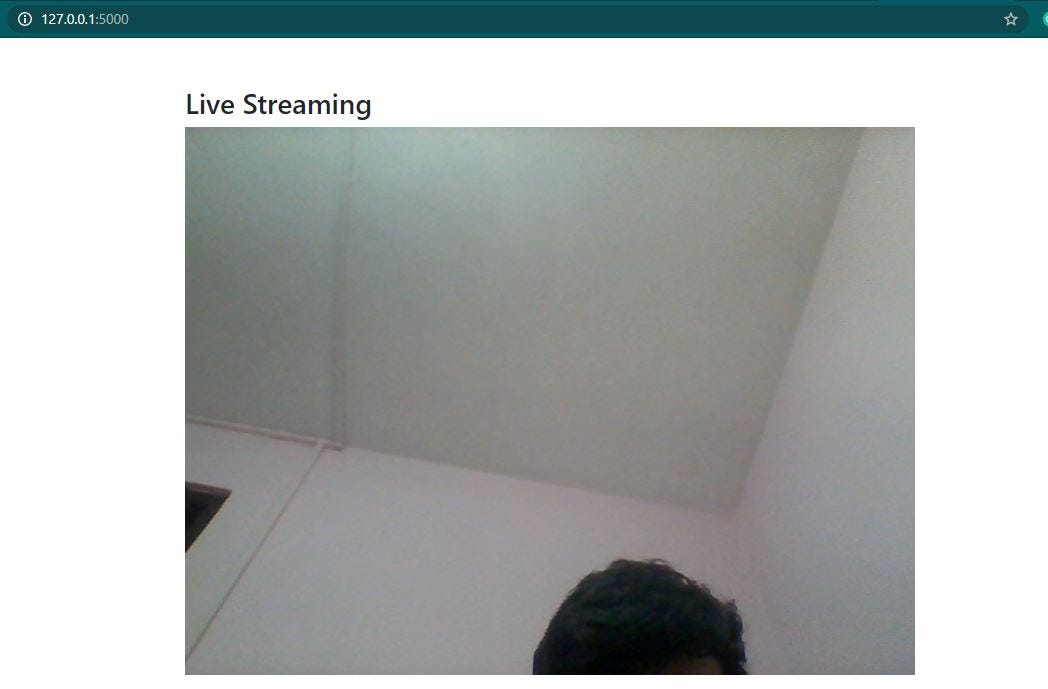
And that'southward it !!
Yous have the alive video stream from your IP camera/webcam on your spider web browser which tin can be used for security and surveillance purposes.

Refer to my GitHub Code.
Note : All the resources that you will require to get started have been mentioned and their links provided in this commodity as well. I hope you make skillful apply of it :)
I hope this commodity will get you interested in trying out new things in the Calculator Vision domain and help yous add to your knowledge. If you have enjoyed reading this article practise share it with your friends and family. Give thanks you for your fourth dimension.
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com/video-streaming-in-web-browsers-with-opencv-flask-93a38846fe00
Posted by: biscoecloons1986.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Connect Video Camera To Computer For Live Streaming"
Post a Comment